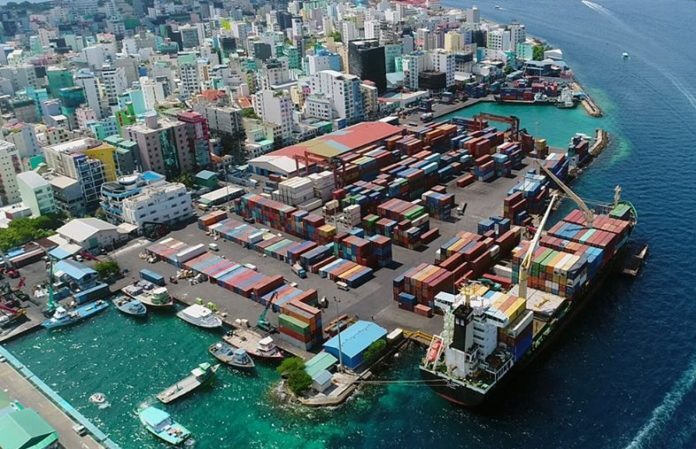
The Maldives, composed of 1200 islands and a population of about 5 hundred thousand people, is highly dependent on imports, mainly for necessities such as food. However, it’s concerning that regardless of having a tourism-driven economy that earns over $3 billion annually, the island nation depends on other countries for an alarming percentage of necessities.
According to the monthly statistics by Maldives Customs Service in May 2020, food items were the largest import category with 373 million imported (excluding alcohol, pork, tobacco). From the necessities imported a majority percentage was taken by staple foods (MVR 358 million) followed by potatoes, onions, and chicken. While total imports for the period (Jan-May 2020) amounted to MVR13.6 billion, the exports were just MVR991 million and total revenue was MVR1.1 billion.
Considering the international trade statistics of the country, worrying over the financial performance of the economy would be justifiable. In fact, the total Government debt outstanding as a percentage of GDP is 75.6% in 2020, an increase of 14.5% from 2019, as per data compiled by the Maldives Monetary Authority, Ministry of Finance, and National Bureau of Statistics.
However, is the country truly incapable of supplying the necessities such as food products to the population? The Maldives is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world with 1.9 million tourist arrivals in 2019 and one of the most highly dependent economies on tourism for its revenue. The MIRA annual report 2018 shows that tourism contributed to 62.2% of GGST and 15.9% of the total Business Profit Tax. While the economy has a successful industry, what could be the reason for the excessive value of imports?
The Maldives is rich in agricultural resources, with the land that can be utilized for various food products. The country also has the potential to improve its human capital in the field by investing in training, education as well as the latest technology. It is highly important that an economy isn’t overdependent on other countries, which was clearly seen from the effects of COVID-19 pandemic in the country.