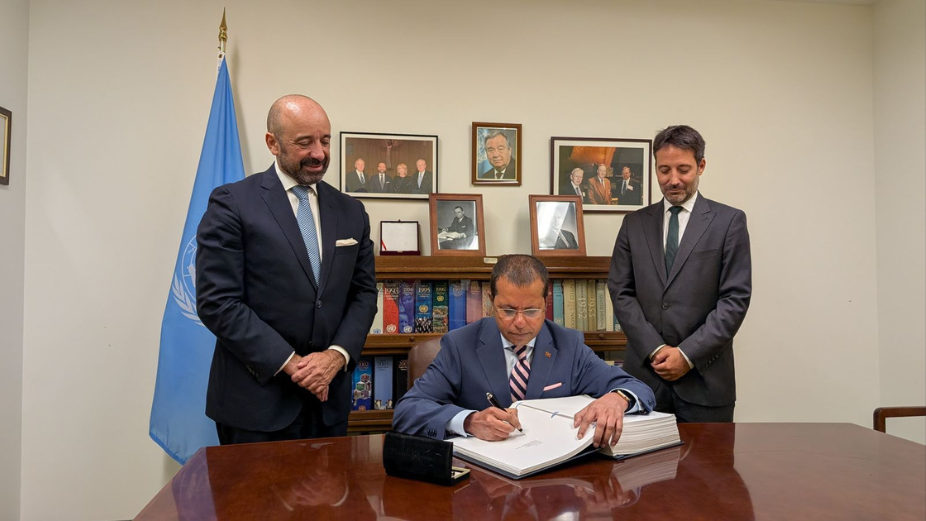
The Maldives has officially become the 92nd signatory of the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, marking a significant step in the country’s commitment to marine conservation. The Agreement was signed by the Permanent Representative to the United Nations, Dr. Ali Naseer Mohamed, at a ceremony held at the United Nations Headquarters in New York on 3 September 2024. The signing follows the Maldivian government’s decision earlier this year to join the global effort to protect marine biodiversity beyond its national jurisdiction.
Understanding the BBNJ Agreement
The BBNJ Agreement is a landmark international treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 19 June 2023, after nearly a decade of negotiations. The Agreement focuses on the protection and sustainable use of marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, often referred to as the high seas. These areas constitute nearly two-thirds of the world’s oceans and are vital for global biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of millions who depend on marine resources.
The Agreement was born out of the need to address the gaps in the current international legal framework concerning the high seas. In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly initiated the development of this legally binding instrument, recognising the importance of conserving marine biodiversity in these largely unregulated waters. Between 2016 and 2023, substantive negotiations took place, culminating in the adoption of the BBNJ Agreement.
Key Provisions and Actions Under the Agreement
Under the BBNJ Agreement, signatory countries commit to a range of measures aimed at safeguarding marine biodiversity beyond their national jurisdictions. One of the core elements of the Agreement is the establishment of large-scale marine protected areas (MPAs) in these international waters. These MPAs will help regulate activities that may pose a threat to marine ecosystems, such as deep-sea mining, overfishing, and pollution, thereby preserving biodiversity and promoting the sustainable use of marine resources.
In addition to establishing MPAs, the Agreement outlines frameworks for the fair sharing of marine genetic resources and includes provisions for capacity building and marine technology transfer. It also addresses the impacts of climate change on the oceans, mandating cooperative efforts to mitigate its effects and ensure sustainable development.
Economic Benefits for the Maldives
As a nation whose economy is deeply intertwined with its marine environment, the Maldives stands to benefit economically from joining the BBNJ Agreement. The Agreement’s framework for marine protected areas could directly enhance the sustainability of the Maldives’ fisheries sector. By ensuring the sustainable management of fish stocks in high seas areas adjacent to its exclusive economic zone (EEZ), the Maldives can potentially secure its fisheries resources, which are vital for domestic consumption and export.
The fisheries sector is not the only beneficiary. The Maldives’ tourism industry, which relies heavily on the country’s pristine marine environments, could also gain significantly. The Agreement’s focus on conservation can be leveraged to attract eco-conscious tourists, a growing market segment in global tourism. This can lead to an expansion in high-value ecotourism, enhancing the Maldives’ reputation as a leader in marine conservation and boosting tourism revenues.
Leveraging Technology and International Cooperation
The BBNJ Agreement also opens avenues for the Maldives to access advanced marine technologies. As part of the Agreement, developed countries are encouraged to share marine technologies and scientific knowledge with developing countries. For the Maldives, this means an opportunity to adopt state-of-the-art technologies that can aid in monitoring, managing, and conserving its marine resources more effectively. Access to such technologies can also enhance the Maldives’ ability to adapt to climate change impacts, which pose a significant threat to its economy and way of life.
Future Prospects and Strategic Considerations
While the BBNJ Agreement is open for signature by all countries until 20 September 2025, it will only enter into force 120 days after the 60th country ratifies it. So far, only eight countries have ratified the Agreement, and the Maldives, having signed it, will need to follow up with ratification to fully commit to its provisions.
Being a signatory places the Maldives at the forefront of global marine conservation efforts. However, it also brings responsibilities that require careful balancing between economic development and environmental sustainability. The Maldives must navigate these new waters with strategic planning, ensuring that its economic activities, particularly in fisheries and tourism, align with the conservation goals set by the Agreement.
The Maldives’ decision to sign the BBNJ Agreement represents not just a commitment to marine conservation but also a forward-looking economic strategy. By participating in this global effort, the Maldives is positioning itself to benefit from sustainable marine resource management, technological advancements, and enhanced international cooperation. If effectively implemented, the BBNJ Agreement could help safeguard the country’s economic future while preserving the natural heritage that is so central to its identity and prosperity.